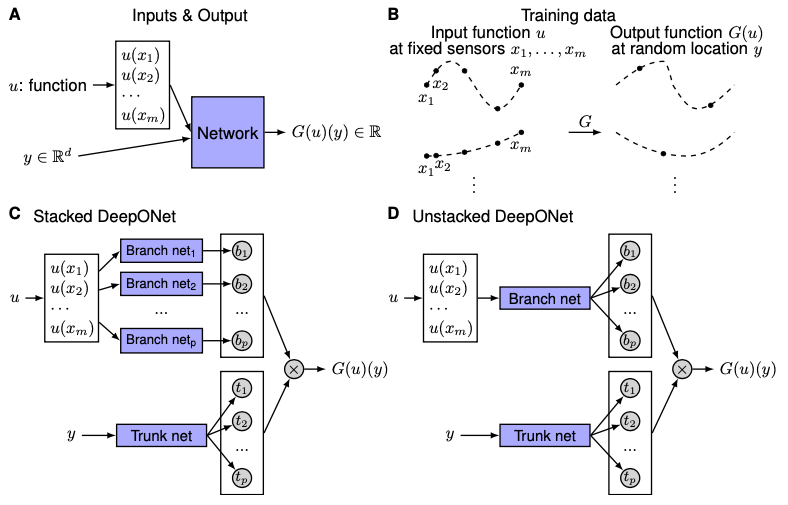
DeepONet
“Inspired from the universal approximation theorem, neural networks with a single layer could not only approximates continuous functions, but also continuous functional or operators”1
Concepts
functional: a mapping from a space of functions into a real number
operator: a mapping from a space of functions to another space of functions
Architecture
What DeepONet wants to do is to form a network to learn functions and points together, different from fully-connected neural networks that only gurantee a small approximation error, and expecting consideration on optimization error and generalization error.
- Inputs
- input functions $u(x_{1}),u(x_{2}),…,u(x_{m})$, will be learnt by (stacked/unstacked) branch net, of which input is $x_{1}, x_{2},…, x_{m}$, also called sensors.
- points
ywill be learnt by trunk net
- Requirements
- consistency of of sensors
- Notice
yandu(x)may be not equally matched in dimensions in high dimensional problems, so two sub-networks are needed.- input function is represented by neural networks.
Notices
- Input functions here were mean-zero Gaussian Random field(GRF) and Orthogonal polynomials, and could be expanded to more than one function.
- number of sensors
mwere derived to be sufficient enough to achieve accuracy, which is set as 100 in the paper.
Personal Opinions
DeepOnet provides a primary method in learning PDEs and ODEs by the input function and seperate points. The input functions may be explicitly expressed by equations or implicitly expressed by networks, which indicates a nested functions that generally appears in the complex phenomena. However,
- the process may lack of interpretability, when explaination is needed for the causality between input and output function.
- Additionally, all sensors from the input function are packaged to be learned by
pbranch nets. What if there are multiple input functions to be learnt? Further, if we don’t know prior knowledge, how do we discern these functions from raw data, to achieve an approximator of mechanisms that learn known knowledge and may discover unknown knowledge.
Further development
- Solved problems
- Unsolved problems
- Without prior knowledge, how could we learn explainable functions with mathematical thinking from raw data?
References
-
DeepXDE. https://deepxde.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/deepxde.nn.tensorflow.html. ↩
-
MIONet: Learning Multiple-Input Operators via Tensor Product. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1137/22M1477751. ↩
-
Learning the solution operator of parametric partial differential equations with physics-informed DeepONets.(2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abi8605. ↩
-
Reliable extrapolation of deep neural operators informed by physics or sparse observations. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2023.116064. ↩